1. What we want to achieve
In this passage, we’re going to discuss about how to build a rest api for openstack sdk on MacOS. The openstack sdk document is very detailed and informational for developer, but this also results in the disadvantage that we are not easy to find out what we want in these tons of documents.
Well, this passage is about how to use NodeJs and openstack sdk to deploy REST API to help us query the instance status, such as instance status, keyname, flavor, image, instance id, name, etc. And we’re going to create a api by openstack sdk for python to to spawn up a new instance.
2. Environment set up
2.1 Install the openstack sdk by pip and Node.js by Homebrew
Install the Node.js by Homebrew
brew install node
Open the terminal and run the below command.
pip install python-openstacksdk
If you fail to install the python-openstacksdk because of the permission, then you can use this command, add --user to the end of previous command and run it again. But the python-openstacksdk only support python3 and which means that you should gurantee that you machine is capable to run python 3.
2.2 Create a configuration file
Modify the username and password to based on your credential in cloud.yaml file, and put this file in the same dierctory as demo.py in the below.
# clouds.yaml
clouds:
mordred:
# Modify the region if necessary
region_name: RegionOne
auth:
# Change username and password to yours.
username: 'xxxxxxx'
password: xxxxxxx
# The porject you are working on the openstack cloud.
project_name: 'CH-817461'
# The url for authorization.
auth_url: 'https://openstack.tacc.chameleoncloud.org:5000/v2.0'
3. Code
3.1 Create a demo.py in the node project directory
We create a python script file named demo.py, the script mainly has two functions, one is to query the status of all instances with instances_status and create a new instance with create_instance. After we finish those functions, we need to conside how to return the result to the program of Node.js. In this program, we only to need to print the result out the program in Node.js will receive the message from stdout.
import openstack.cloud
import sys
# Enable the debug mode
openstack.enable_logging(debug=True)
connection = openstack.connect(cloud='mordred')
# Spawn an instance .
# Change the value of parameter if necessary
def create_instance(instanceName="testInstance",
imageName="CC-Ubuntu16.04",
keypairName="rsa_key",
flavorName="m1.small",
securityGroups="Restricted IPv4"
):
image = connection.compute.find_image(imageName)
keypair = connection.compute.find_keypair(keypairName)
flavor = connection.compute.find_flavor(flavorName)
# Wait for the creation
server = connection.create_server(
instanceName,
image=image,
flavor=flavor,
wait=True,
auto_ip=True,
key_name=keypair.name,
security_groups=[securityGroups])
print(server)
# Construct instance info base on ServerDetail Object
def convert_serverDetail_json(server):
result = {}
result['status'] = server.status
result['key_name'] = server.key_name
result['image'] = server.image
result['flavor'] = server.flavor
result['id'] = server.id
result['user_id'] = server.user_id
result['name'] = server.name
return result
# Query the instance status
def instances_status():
for server in connection.compute.servers():
print(convert_serverDetail_json(server))
# handle the different request
def do_request(command, args):
if command == 'instances_status':
instances_status()
elif (command == 'create_instance'):
create_instance(args[0], args[1], args[2], args[3], args[4])
else:
print("No operation for this parameter")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Read parameters from node
input_from_node = sys.stdin.readline().strip()
spilt_data = input_from_node.split(",")
command = spilt_data[0]
args = spilt_data[1:]
do_request(command, args)
3.2 Create a node project
- Dependency:
express~4.16.0python-shell~0.5.0
And we can first create a diectory with arbitrary name and enter that directory, then create a index.jsfile and use npm to initialize the project. For the index.js file we will implement in the following way. The main idea of the following code is to use python-shell module to communicate with python program. Every time we get a request from the client, we send the parameters to the program, and the python program will get the parameters from stdin . After being processed by demo.py, the node program will receive the message from the stdout of python, which is the entire procedure followed by the communication between nodejs program and python script program.
// Packages SET UP
var express = require('express')
var PythonShell = require('python-shell')
var app = express()
// ROUTE CONFIG
var router = express.Router();
// Python environment configuration
var pyoptions = {
mode: 'text',
pythonPath:'/usr/local/bin/python3.6',
scriptPath:'./'
};
// Python script option
var scriptOption = {
'demo':'demo.py'
};
// Application-level middleware
router.use(function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Time:', Date.now());
next();
});
// set up SERVER and base route
router.get('/', function(req, res) {
res.send("This is a new world that you r looking for.");
});
// Look up running openstack computing instances
router.route('/instances_status')
.get(function (req, res){
var shell = new PythonShell(scriptOption['demo'],pyoptions);
// Send text message to python program
shell.send("instances_status");
var result = [];
shell.on('message', function(message){
result.push(message);
});
shell.end(function(err, code, signal) {
if (err) throw err;
res.send(result);
console.log("The exit code is: "+code);
console.log("The exit signal is: "+signal);
});
});
// Create an openstack computing instance
router.route('/create_instance')
.get(function(req, res){
var shell = new PythonShell(scriptOption['demo'],pyoptions);
// Send text message to python program
var separator = ",";
var result = " ";
var msg = "create_instance" + separator
+ req.query.instanceName + separator
+ req.query.imageName + separator
+ req.query.keypairName + separator
+ req.query.flavorName + separator
+ req.query.securityGroup;
shell.send(msg);
shell.on('message', function(message){
result = message;
});
shell.end(function(err, code, signal) {
if (err) throw err;
res.send(result);
console.log("The exit code is: "+code);
console.log("The exit signal is: "+signal);
});
});
// register route
app.use('',router);
// START UP SERVER
var server = app.listen(8081, function(){
var host = server.address().address;
var port = server.address().port;
console.log(" Example app listenning at http://%s:%s", host, port);
});
4. Run the project
4.1 Spawn up the server and run index.js
node index.js
4.2 run with the program with
-
Run the request for instance status
The response will be a list of instances of basic info.
http://[server_ip]:[8081]/instances_statusAnd we will get the response
{ 'status':'ACTIVE', 'key_name':'rsa_key', 'image':{ 'id':'30adb881-xxx-xxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx', 'links':[ { 'href':'http://openstack.tacc.chameleoncloud.org:8774/CH-817461/images/xx', 'rel':'bookmark' } ] }, 'flavor':{ 'id':'5', 'links':[ { 'href':'http://openstack.tacc.chameleoncloud.org:8774/CH-817461/flavors/5', 'rel':'bookmark' } ] }, 'id':'180d59fa-9c34-495e-b3c8-e7bf1f9e6418', 'user_id':'superman', 'name':'TensorFlow_Platform' } -
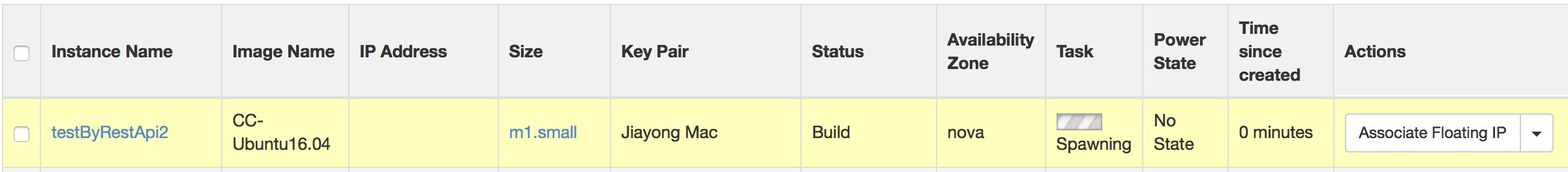
Run the request for instance creation
The reposne will be the detailed information of the new instance.
http://[server_ip]:[8081]/create_instance?instanceName=testByRestApi2&imageName=CC-Ubuntu16.04 / &keypairName=rsa_key&flavorName=m1.small&securityGroup=Restricted IPv4And an instance will be spawned on the openstack cloud.


Leave a Comment